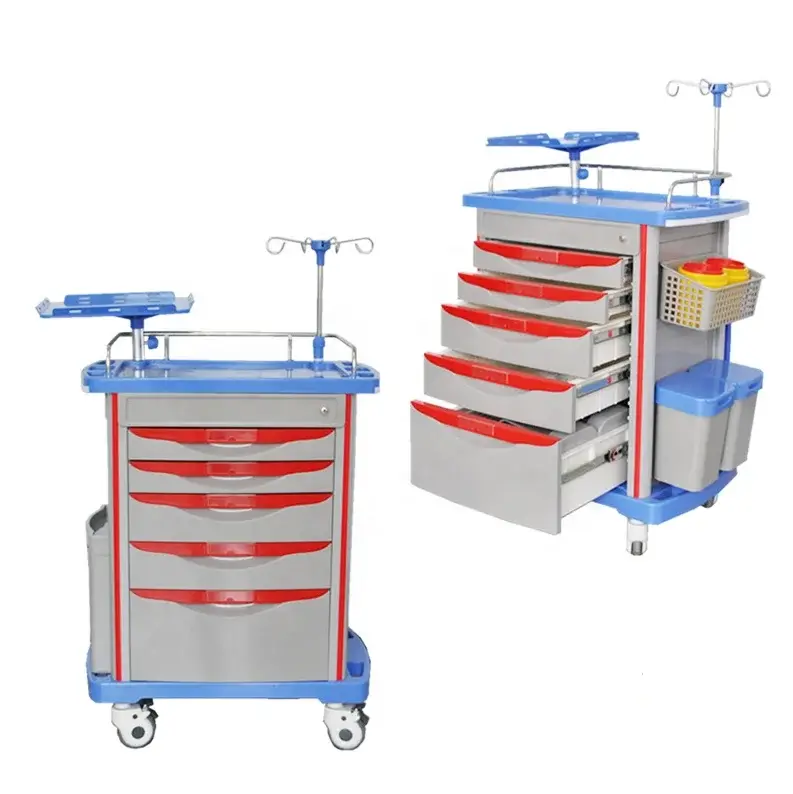
Clinical Trolley Design for Infection Control and Hygiene
Clinical trolleys are indispensable in healthcare, used for transporting various items such as medical instruments, pharmaceuticals, and patient samples. However, their role extends beyond efficient transportation; they are a potential source of infection spread. Traditional trolleys, often made of porous materials, can harbor bacteria and viruses, posing risks to both patients and staff. The design of these trolleys, including their materials, structure, and mechanisms, significantly influences their ability to prevent contamination. For instance, trolleys equipped with wheels designed to glide smoothly over surfaces may inadvertently spread bacteria, whereas those with non-porous, antimicrobial surfaces could offer better protection. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for designing trolleys that not only transport items but also safeguard infection control processes.
Hygiene Considerations in Clinical Trolley Design
The materials and features of clinical trolleys bear direct implications for hygiene. Porous materials, while convenient, can become breeding grounds for bacteria and viruses, making them a hazard. On the other hand, non-porous materials, such as antimicrobial fabrics or materials resistant to liquids, offer superior hygiene benefits. Additionally, the presence of easy-to-clean components is essential. Trolleys with wheels that can be quickly cleaned or retractable baskets that facilitate disinfection are preferable over those with permanent fixtures that may remain contaminated. Furthermore, the design's ergonomics plays a role; ergonomically designed trolleys are easier to use, reducing the risk of hand contact during transport. Integrating these considerations into design specifications can significantly enhance the hygiene effectiveness of clinical trolleys.

Design Innovations for Enhanced Infection Control
Innovative design features are revolutionizing clinical trolley design, addressing the challenges of infection control. Features such as antimicrobial coatings, which kill bacteria upon contact, and UV light sterilization capabilities are breaking new ground. Touchless operation, where trolleys are designed to avoid physical contact, is another significant advancement, reducing the risk of contamination. Additionally, integrated sensors that monitor contamination levels and automatically clean trolleys can enhance hygiene. Studies have shown that trolleys with antimicrobial coatings can reduce contamination rates by up to 90%, highlighting the transformative potential of such innovations.
Comparative Analysis of Current vs. New Designs
A comparative analysis of current and new clinical trolley designs reveals stark differences in their effectiveness. Traditional trolleys, with their porous materials and limited cleaning features, often lead to higher infection rates, as evidenced by recent studies. In contrast, newer designs, equipped with antimicrobial surfaces and advanced cleaning mechanisms, demonstrate significant improvements. Case studies from healthcare facilities implementing antimicrobial trolleys report a 20-30% reduction in contamination incidents. This comparative analysis underscores the necessity of adopting innovative designs to meet infection control standards, emphasizing the importance of evaluating design features thoroughly before implementation.
Best Practices for Specifying Clinical Trolleys for Infection Control
Selecting the right clinical trolley design requires careful consideration of specific needs and adherence to infection control standards. When specifying trolleys, it is essential to assess the types of equipment and supplies being transported, ensuring that the trolley design aligns with their hygiene requirements. Compliance with regulatory standards and using standardized specifications can enhance the reliability and effectiveness of trolleys. Additionally, verifying manufacturer certifications and warranties is crucial, as reputable brands often adhere to stringent hygiene and quality control practices. Engaging with healthcare providers and safety experts can also provide valuable insights, ensuring that trolley selection supports infection control measures.
Future Trends in Clinical Trolley Design for Hygiene
The future of clinical trolley design is brimming with potential, driven by emerging technologies and sustainable materials. Robotics and AI integration are expected to play a pivotal role, optimizing trolley operations and enhancing hygiene. For instance, AI-driven systems could predict contamination risks and automatically clean trolleys in real-time. Sustainable materials, such as recycled plastics and biodegradable fabrics, are anticipated to emerge, offering eco-friendly solutions that prioritize hygiene. Furthermore, advancements in trolley automation could reduce the need for manual handling, minimizing the risk of hand contact and enhancing safety. These trends herald a new era of innovative and hygienic clinical trolleys, set to transform healthcare operations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, optimizing clinical trolley design for infection control and hygiene is a multifaceted endeavor that demands careful consideration of materials, features, and innovation. By adopting best practices and embracing future trends, healthcare facilities can enhance the hygiene effectiveness of their trolleys, ultimately contributing to safer and more hygienic patient care. The journey to achieving this goal is ongoing, driven by technological advancements and a commitment to excellence. As we move forward, it is essential to stay informed about new developments and apply these innovations in ways that best suit our needs. By prioritizing clinical trolley design, we can create a healthcare environment where infection control and hygiene are at the forefront, safeguarding both patients and staff.